HIP
Conditions
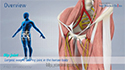
Hip Anatomy
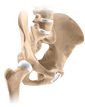
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the human body. It is also referred to as a ball and socket joint and is surrounded by muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The thigh bone or femur and the pelvis join to form the hip joint.
Hip Pain
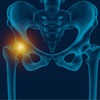
Hip pain, one of the common symptoms patients complain of, may not always be felt precisely over the hip joint. Pain may be felt in and around the hip joint and the cause for pain is multifactorial. The exact position of your hip pain suggests the probable cause or underlying condition causing pain. Pain felt inside the hip joint or your groin area is more likely to be because of the problems within the hip joint.
Labral Tears
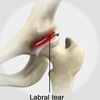
A hip labral tear is an injury to the labrum, the cartilage that surrounds the outside rim of your hip joint socket. The hip joint is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The labrum helps to deepen the socket and provide stability to the joint. It also acts as a cushion and enables smooth movements of the joint.
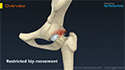
FAI – Femoro Acetabular Impingement
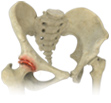
Femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) is a condition in which the bones of the hip joint grow abnormally and do not fit together properly. This leads to restricted hip movement and increased friction between the ball and socket of the hip joint resulting in damage to the joint.
Hip Developmental Dysplasia
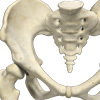
Developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH) is a common disorder that is seen in infants and young children. It may be present at birth or may occur during the first year of life of the infant. As the name suggests, it occurs due to improper development of the hip joint either while the fetus is in the uterus or during the growth phase in the first year of life.
Loose Bodies
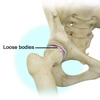
Loose bodies are small loose fragments of cartilage or a bone that float around the joint. The loose bodies can cause pain, swelling, locking and catching of the joint. Loose bodies occur if there is bleeding within the joint, death of tissues lining the joints associated with tuberculosis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Hamstring Avulsions
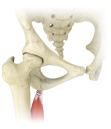
Hamstring injuries are common in athletes who participate in sports activities such as track, soccer, and basketball that involve running,. The three hamstring muscles namely semitendinosus, semimembranosus and biceps femoris are at the back of the thigh and helps you bend (flex) your knee and extend your leg.
Avascular Necrosis
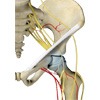
Avascular necrosis, also known as AVN and osteonecrosis, is a disease caused from inadequate blood supply to the bone which leads to bone death.
This disease is most common in adults aged 30-60 but can also occur in children, mainly from cancer therapy. It can affect one or more bones and if left untreated, it can lead to destruction of the adjacent bones, tissues and joints.
Chondral Lesions or Injuries
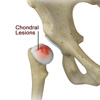
The hip joint is one of the largest weight-bearing joints in the body, formed by the thigh bone or femur and the acetabulum of the pelvis. It is a ball and socket joint with the head of the femur as the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forming the socket. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular cartilage which acts as a cushion and enables smooth movements of the joint. A chondral injury refers to an injury of the articular cartilage, covering the joint.
Gluteus Medius Tear
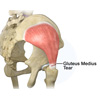
The gluteal muscles are a major group of muscles located at the back of the pelvis forming the buttocks that helps in the stability of the hip. The gluteal muscles comprise of three muscles: gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and the gluteus minimus. These muscles facilitate in abduction, extension, internal and external rotational movements of the hip.
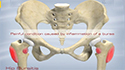
Hip Bursitis
Greater trochanter bursitis also called hip bursitis is a common problem caused by inflammation of the bursa that overlies the greater trochanter (bony prominence at the outer side of the hip). A bursa is a small sac filled with fluid which acts as a cushion and allows smooth motion by reducing the friction between the muscles and the bone. The condition causes pain in the outer portion of the upper thigh.
Hip Instability
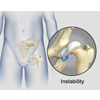
The hip plays an important role in supporting the upper body weight while standing, walking and running, and hip stability is crucial for these functions. The femur (thigh bone) and acetabulum (hip bone) join to form the hip joint, while the labrum (tissue rim that seals the hip joint) and the ligaments lining the hip capsule maintain the stability of the hip. Injury or damage to these structures can lead to a condition called hip instability. Hip instability happens when the hip joint becomes unstable causing various symptoms.
Irritable Hip
Irritable hip, also known as acute transient synovitis, is a common disorder of childhood characterized by onset of hip pain and limping. The term transient means that it does not usually last long. It usually occurs before puberty and affects only one hip. Boys aged between 4 to 10 years are most often affected 2 to 4 times more than girls.
Hip Muscle Strain
A tear in the muscle fibers caused by either a fall or direct blow to the muscle, overstretching and overuse injury is called a strain. Muscle strains often occur in the hip region whenever a muscle contracts suddenly from its stretched position. It can be mild, moderate or severe and depends on the level of injury. The chances of having a hip muscle strain becomes high if you have had a previous injury in the area or if there is no warm-up before exercising.
Videos
Procedures
Hip Arthroscopy

Hip arthroscopy, also referred to as keyhole surgery or minimally invasive surgery, is performed through very small incisions to evaluate and treat a variety of hip conditions. Arthroscopy is a surgical procedure in which an arthroscope is inserted into a joint. Arthroscopy is a term that comes from two Greek words, arthro-, meaning joint, and -skopein, meaning to examine.
Cartilage Repair
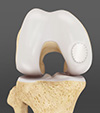
The hip joint is the largest weight-bearing joint in the body. It is a ball and socket joint where the head of the femur (thigh bone) is the ball and the pelvic bones form a socket called the acetabulum. The bone surfaces in the joint are covered by smooth cartilage which acts as a cushion and enables the bones to easily glide over each other during movement. A rim of cartilage called the labrum is present at the edge of the socket and increases the depth of the socket providing stability to the joint.
Proximal Hamstring Repair
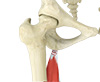
The hamstring muscles are three muscles at the back of the thigh that are commonly injured during sports that involve running, jumping and sudden changes in speed. Injury usually occurs at the proximal tendinous origin of the muscles which attach to the ischium, a pelvic bone. The risk of injury increases with age, prior injury, lack of flexibility and being overweight.